Ultrasonic Flowmeter Principles and Technology
Ultrasonic waves are inaudible to our ears. Aichi Clock Electric has been developing flow meters (gas meters) that measure flow rates by utilizing the characteristics of this ultrasonic wave. Some of the technologies we are proud of are briefly introduced below!
What is an "Ultrasonic Flowmeter" (measures flow using ultrasonic waves)
Generally, sound waves that cannot be heard by the human ear are called "Ultrasonic waves". Ultrasonic waves have characteristics similar to those of light, such as straightness, reflection, and generation of energy by vibration. Traditionally, membrane or impeller type flow meters have been used to measure the flow rate of gases and liquids, but Aichi Tokei Denki is developing an "Ultrasonic Flowmeter" that transmits and receives ultrasonic waves and measures the flow rate by accurately measuring the time taken for the sound waves to travel.

Measuring principle of "Ultrasonic flowmeter"
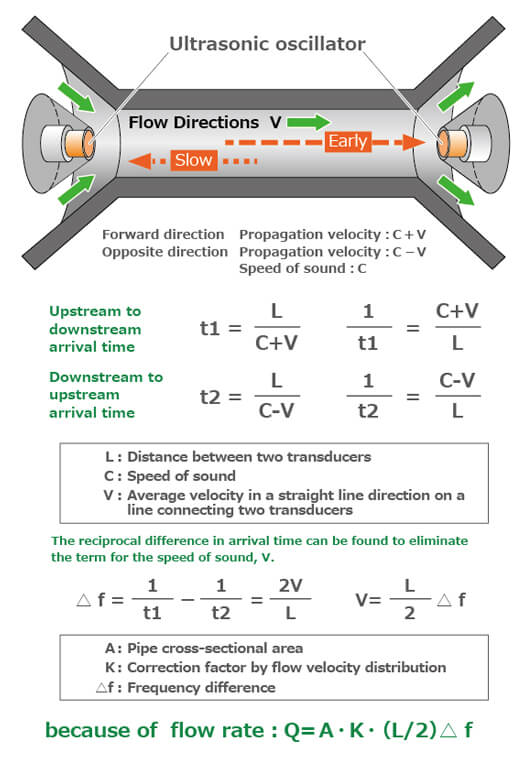
A set of ultrasonic sensors is placed upstream and downstream of each other in a conduit through which fluid flows, and the arrival time of sound waves transmitted between them is measured.
Schematically, when playing catch in windy conditions, if the ball is thrown (sound waves are emitted) from upwind, it will arrive earlier because of less wind resistance, and if it is thrown from downwind, it will arrive later because of wind resistance. The difference in the transmission time of sound waves emitted from upwind or downwind is proportional to the speed at which the fluid flows. The ultrasonic flowmeter calculates the flow velocity along the ultrasonic wave path by measuring the arrival time of sound waves transmitted in the pipeline, and outputs the flow rate by multiplying it by a correction factor for the cross-sectional area of the pipeline and the velocity distribution.
The actual time difference is very small, ranging from a few nanoseconds at 3L/h for gas to several tens of microseconds at 6,000L/h.
Realization of "miniaturization" and contribution to "safety and security"
The operating principle of the membrane gas meter, one of the major gas flowmeters in use today, is to measure the volume of a rubber balloon by inflating and deflating it, which requires multiple rubber balloons to operate efficiently, making it a large device.
In contrast, ultrasonic flowmeters have a simple structure with only a set of ultrasonic sensors in the fluid flow, and thus can be made much smaller. In particular, Diaphragm types gas meters for commercial use require large-capacity rubber balloons, so the downsizing achieved by the ultrasonic type is even more pronounced.
Also, to measure a slight flow caused by gas leakage, the membrane type requires time for the rubber balloon to inflate, whereas the ultrasonic type takes almost no time at all, since the time difference is measured. The ultrasonic method can detect gas leaks in a shorter time, contributing to safety and security.
The "ultrasonic method" is a highly promising measurement method in the field of measurement, where low cost and high added value are required, regardless of whether the measurement is of gases or liquids. Aichi Tokei Denki will continue to develop a variety of measuring instruments that take advantage of the characteristics of ultrasonic waves.
■ Flow Meters and Related Products|Click here to see the lineup of ultrasonic flowmeters
Inquiries about research and development of the latest technologies
Aichi Tokei Denki Co.,Ltd.
Please contact us using the General Inquiry Form.